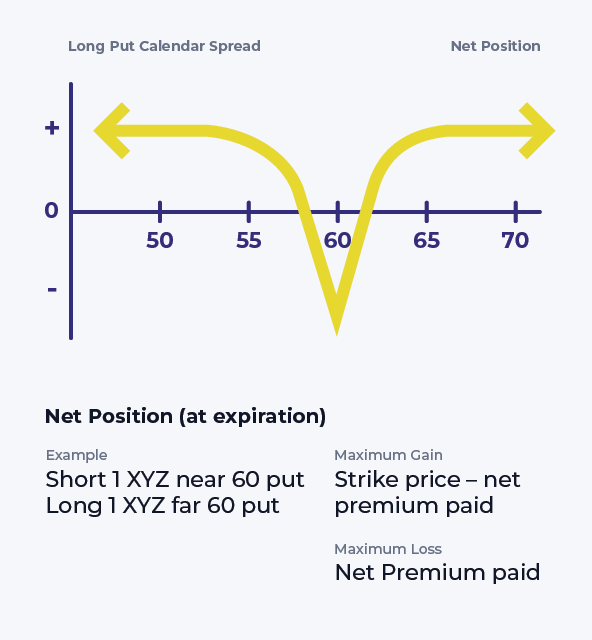
Put Calendar Spread - A put calendar spread is an options strategy that combines a short put and a long put with the same strike price, at different expirations. There are inherent advantages to trading a put calendar over a call calendar, but both are readily acceptable trades. A diagonal spread allows option traders to collect premium and time decay similar to the calendar spread, except these trades take a directional bias. A calendar spread typically involves buying and selling the same type of option (calls or puts) for the same underlying security at the same strike price, but at different (albeit small differences in) expiration dates. A calendar spread is an options or futures strategy where an investor simultaneously enters long and short positions on the same underlying asset but with different delivery dates. When running a calendar spread with puts, you’re selling and buying a put with the same strike price, but the put you buy will have a later. This type of strategy is also known as a time or horizontal spread due to the differing maturity dates. A calendar spread allows option traders to take advantage of elevated premium in near term options with a neutral market bias. If a trader is bullish, they would buy a calendar call spread. There are two types of long calendar spreads:
Put Calendar Spread
A long calendar spread with puts is the strategy of choice when the forecast is for stock price action near the strike price of the spread, because the strategy profits from time decay. Whether a trader uses calls or puts depends on the sentiment of the underlying investment vehicle. There are two types of long calendar spreads: When running a.
Put Calendar Spread Guide [Setup, Entry, Adjustments, Exit]
This type of strategy is also known as a time or horizontal spread due to the differing maturity dates. A long calendar spread with puts is the strategy of choice when the forecast is for stock price action near the strike price of the spread, because the strategy profits from time decay. There are two types of long calendar spreads:.
Bearish Put Calendar Spread Option Strategy Guide
A diagonal spread allows option traders to collect premium and time decay similar to the calendar spread, except these trades take a directional bias. A calendar spread typically involves buying and selling the same type of option (calls or puts) for the same underlying security at the same strike price, but at different (albeit small differences in) expiration dates. When.
Put Calendar Spread Option Alpha
A diagonal spread allows option traders to collect premium and time decay similar to the calendar spread, except these trades take a directional bias. A calendar spread is an options or futures strategy where an investor simultaneously enters long and short positions on the same underlying asset but with different delivery dates. When running a calendar spread with puts, you’re.
Short Put Calendar Short put calendar Spread Reverse Calendar
When running a calendar spread with puts, you’re selling and buying a put with the same strike price, but the put you buy will have a later. Whether a trader uses calls or puts depends on the sentiment of the underlying investment vehicle. A long calendar spread with puts is the strategy of choice when the forecast is for stock.
Put Calendar Spread Guide [Setup, Entry, Adjustments, Exit]
A calendar spread is an options or futures strategy where an investor simultaneously enters long and short positions on the same underlying asset but with different delivery dates. A long calendar spread with puts is the strategy of choice when the forecast is for stock price action near the strike price of the spread, because the strategy profits from time.
Long Put Calendar Spread (Put Horizontal) Options Strategy
There are two types of long calendar spreads: This type of strategy is also known as a time or horizontal spread due to the differing maturity dates. A calendar spread typically involves buying and selling the same type of option (calls or puts) for the same underlying security at the same strike price, but at different (albeit small differences in).
Long Calendar Spread with Puts Strategy With Example
A diagonal spread allows option traders to collect premium and time decay similar to the calendar spread, except these trades take a directional bias. If a trader is bullish, they would buy a calendar call spread. This type of strategy is also known as a time or horizontal spread due to the differing maturity dates. A calendar spread is an.
A long calendar spread with puts is the strategy of choice when the forecast is for stock price action near the strike price of the spread, because the strategy profits from time decay. A calendar spread typically involves buying and selling the same type of option (calls or puts) for the same underlying security at the same strike price, but at different (albeit small differences in) expiration dates. Whether a trader uses calls or puts depends on the sentiment of the underlying investment vehicle. A put calendar spread is an options strategy that combines a short put and a long put with the same strike price, at different expirations. A diagonal spread allows option traders to collect premium and time decay similar to the calendar spread, except these trades take a directional bias. A calendar spread is an options or futures strategy where an investor simultaneously enters long and short positions on the same underlying asset but with different delivery dates. When running a calendar spread with puts, you’re selling and buying a put with the same strike price, but the put you buy will have a later. There are inherent advantages to trading a put calendar over a call calendar, but both are readily acceptable trades. A calendar spread allows option traders to take advantage of elevated premium in near term options with a neutral market bias. There are two types of long calendar spreads: This type of strategy is also known as a time or horizontal spread due to the differing maturity dates. If a trader is bullish, they would buy a calendar call spread.
There Are Two Types Of Long Calendar Spreads:
A diagonal spread allows option traders to collect premium and time decay similar to the calendar spread, except these trades take a directional bias. A long calendar spread with puts is the strategy of choice when the forecast is for stock price action near the strike price of the spread, because the strategy profits from time decay. A put calendar spread is an options strategy that combines a short put and a long put with the same strike price, at different expirations. A calendar spread typically involves buying and selling the same type of option (calls or puts) for the same underlying security at the same strike price, but at different (albeit small differences in) expiration dates.
When Running A Calendar Spread With Puts, You’re Selling And Buying A Put With The Same Strike Price, But The Put You Buy Will Have A Later.
This type of strategy is also known as a time or horizontal spread due to the differing maturity dates. If a trader is bullish, they would buy a calendar call spread. Whether a trader uses calls or puts depends on the sentiment of the underlying investment vehicle. A calendar spread is an options or futures strategy where an investor simultaneously enters long and short positions on the same underlying asset but with different delivery dates.
A Calendar Spread Allows Option Traders To Take Advantage Of Elevated Premium In Near Term Options With A Neutral Market Bias.
There are inherent advantages to trading a put calendar over a call calendar, but both are readily acceptable trades.


![Put Calendar Spread Guide [Setup, Entry, Adjustments, Exit]](https://i2.wp.com/assets-global.website-files.com/5fba23eb8789c3c7fcfb5f31/6019b83133ac2d32ef084fa5_TsbQgZxQ0e-zKJ9h6Fa7azNlnvn0zH-UBlX3l7hriHll2es1fvyFY5N-nOyM1153MJ4wXLNIhH4zanFkJQB0mpqs81lwEBIvqa7IZQRPWXZY1i3J7vV3BpTIL3v5nCyqn-CEbq2U.png)



![Put Calendar Spread Guide [Setup, Entry, Adjustments, Exit]](https://i2.wp.com/assets-global.website-files.com/5fba23eb8789c3c7fcfb5f31/607da29411b814023198cd31_Put-Calendar-Spread-Options-Strategies-Option-Alpha-Handbook.png)